Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a group of inherited disorders that impact the connective tissues in the body, primarily affecting the skin, joints, and blood vessels. 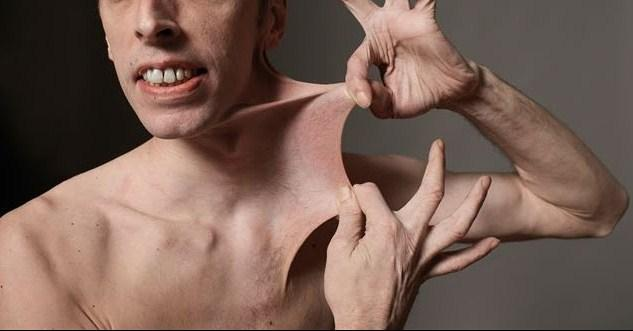

Table of Contents
Introduction
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS) is a group of inherited disorders that impact the connective tissues in the body, primarily affecting the skin, joints, and blood vessels. Characterized by hyperflexibility of the joints, bruising, and hyperextensible skin, EDS presents a myriad of challenges for those diagnosed with it. This article aims to delve into the complexities of EDS, exploring its underlying causes, symptoms, various types, and management strategies.
What is Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome?
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is rooted in a molecular abnormality of collagen, the fundamental protein that provides support to connective tissues. The disorder can manifest in multiple ways and is classified into several types, each with distinct characteristics. Understanding these classifications is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
There are several recognized types of EDS, including:
- Classical EDS: Commonly presents with skin hyperextensibility, easy bruising, and atrophic scars. Patients often exhibit joint hypermobility.
- Hypermobility EDS (hEDS): The most prevalent form, characterized by generalized joint hypermobility without the skin features seen in classical EDS.
- Vascular EDS: This type is notable for severe bleeding and cardiovascular complications, such as arterial rupture. Early-onset periodontal disease is more noticeable in this variant.
- Kyphoscoliotic EDS: Characterized by severe scoliosis and a risk of rupture of the aorta.
- Other Rare Types: There are additional types, such as arthrochalasia EDS and dermatosparaxis EDS, each with unique presentations.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
The symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can vary significantly depending on the type. Common features include:
- Joint hypermobility: Excessive range of motion in joints, leading to an increased risk of dislocations and injuries.
- Skin changes: Individuals may experience velvety, stretchy skin that is fragile and bruises easily.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Problems such as constipation or early satiety may also arise due to reduced collagen in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Vascular complications: In certain types, such as Vascular EDS, there is a heightened risk of internal bleeding.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing EDS typically involves a comprehensive medical history, a physical examination to assess joint hypermobility, and genetic testing to identify specific collagen abnormalities. The Beighton Score, a 9-point scale, is commonly used to evaluate hypermobility in the joints.
Management and Treatment
While there is currently no cure for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, several management strategies can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Physical Therapy: Tailored exercise programs can strengthen muscles around hypermobile joints, helping to provide stability and support.
- Pain management: Medications may be prescribed for chronic pain, which is common in many EDS patients. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are often used.
- Lifestyle modifications: Patients are usually advised to avoid high-impact activities that could lead to joint injury.
- Regular monitoring: Patients, especially those with Vascular EDS, should undergo regular cardiovascular check-ups to monitor for changes in blood vessel integrity.
- Genetic counseling: Families affected by EDS may benefit from genetic counseling to understand the inheritance patterns, especially if planning for children.
Living with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
Living with Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome can be challenging, requiring individuals to navigate both physical and emotional hurdles. Support groups and patient organizations provide resources, advocacy, and a community where individuals can share experiences and gain insights.
Conclusion
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome is a complex disorder that significantly impacts the lives of those affected. Understanding the underlying collagen abnormalities, recognizing the different forms of EDS, and adopting effective management strategies are vital steps in improving the quality of life for patients. As research continues and awareness grows, it is essential for individuals with EDS to seek comprehensive care and support to navigate this condition effectively. While the road may be challenging, with the right tools and knowledge, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite the obstacles posed by Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.
Tags
syndromes


