Marfan Syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissues in the body. Characterized by a range of distinct physical features and associated health issues, this autosomal dominant condition presents unique challenges for those who live with it.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Marfan Syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissues in the body. Characterized by a range of distinct physical features and associated health issues, this autosomal dominant condition presents unique challenges for those who live with it. Notably prevalent among tall athletes, such as basketball and volleyball players, Marfan Syndrome has garnered attention not only for its distinctive symptoms but also for the implications it carries for those who are professionally active in high-impact sports.
What is Marfan Syndrome?
Marfan Syndrome is caused by a mutation in the FBN1 gene, which encodes the connective protein fibrillin-1. This condition affects approximately 1 in 5,000 individuals, emphasizing its significant yet underrecognized impact on health. The symptoms and severity of Marfan Syndrome can vary widely from person to person, but they generally include:
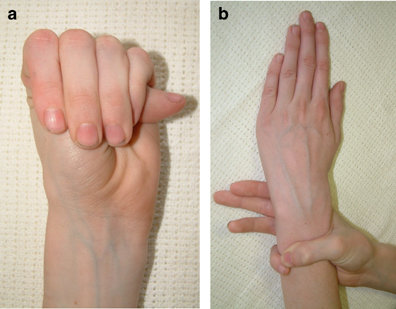
1. Tall, Thin Stature: Individuals often appear taller than their peers, with an elongated body and limbs.
3. Vision Problems: Many patients suffer from dislocated lenses (ectopia lentis), leading to vision impairment.
4. Cardiovascular Complications: Individuals are at risk for serious heart-related issues such as:
- Dissecting aneurysms of the thoracic aorta
- Aortic regurgitation
- Floppy mitral valve
5. Skeletal Abnormalities: A high-arched palate and joint laxity are common, contributing to an increased risk of injury.
Physical Features and Diagnosis
Diagnosing Marfan Syndrome typically involves a combination of physical examinations and genetic testing. Due to the variability in symptoms, healthcare professionals may follow a set of criteria known as the Ghent criteria, which include:
1. Cardiovascular Features: Aortic dilation or regurgitation.
2. Skeletal Features: Proportional measurements such as arm span exceeding height, and skeletal deformities like scoliosis.
3. Ocular Features: Presence of lens dislocation and other vision issues.
4. Family History: Documented occurrences of Marfan Syndrome in relatives.
Doctors may use advanced imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, to assess cardiovascular involvement, as well as genetic testing to confirm mutations in the FBN1 gene. Early diagnosis is crucial for timely management of the associated medical issues.
Implications in Sports
The tall, slender physique associated with Marfan Syndrome often coincides with the physical attributes desired in elite athletes, particularly in sports like basketball and volleyball. While these athletes may excel due to their height and agility, they must also navigate the risks posed by their condition.
It's important to recognize the dual nature of Marfan Syndrome in the athletic population:
1. Athletic Potential: Heightened abilities in sports due to long limbs and agility.
2. Health Risks: Increased cardiovascular risks, including sudden cardiac events.
Consequently, it is essential for athletes with Marfan Syndrome to engage in careful discussions with healthcare providers about their level of participation in competitive sports. Screening for cardiovascular problems and consistent monitoring is critical to mitigate risks.
Living with Marfan Syndrome
Embracing a proactive approach towards managing Marfan Syndrome can significantly enhance quality of life. Individuals diagnosed with this condition can take several steps, including:
1. Regular Medical Check-ups: Routine cardiovascular evaluations to monitor the heart and aorta.
2. Genetic Counseling: Understanding inheritance patterns and implications for family planning.
3. Tailored Exercise Programs: Engaging in low-impact physical activities to maintain fitness while minimizing injury risks.
4. Mental Health Support: Connecting with support groups and mental health professionals to cope with the challenges of living with a chronic condition.
By educating themselves and actively participating in their healthcare, individuals with Marfan Syndrome can lead fulfilling lives while managing their unique challenges.
Conclusion
Marfan Syndrome is a complex genetic condition that, while often associated with athletes, poses significant health risks that must be addressed with care. An increased understanding of its symptoms, diagnosis, and implications can facilitate better management strategies. Through early intervention, support, and education, individuals with Marfan Syndrome can successfully navigate life’s challenges, harnessing their unique physical attributes while ensuring their health remains a priority. As awareness grows, so does the hope for those affected by this condition to live vibrant, active lives.
Tags
syndromes